How Much Money Does Doordash Make
Executive Summary:
DoorDash is an online food delivery service, which partners up with local restaurants to deliver meals to customers nearby. Deliveries are executed by contractual drivers (so-called Dashers) that operate on an on-demand basis.
DoorDash makes money via commissions, delivery and service fees, a white-label logistics service, premium subscription plans, as well as by providing a catering service for businesses customers.
Founded in 2013 by four Stanford graduates, DoorDash became an instant success with customers due to its flexible workforce of drivers. The company went public in December 2020, making it one of the largest IPO's in the food delivery industry.
How Does DoorDash Work?
DoorDash is an on-demand food delivery platform that allows customers to order food and beverages from restaurants nearby. People can order through the company's website or their Android and iOS apps respectively.
DoorDash does not prepare the food themselves. Instead, the company partners up with local restaurants and big food chains across the US to serve people in metropolitan areas.
In some instances, DoorDash will provide kitchen space for the restaurant to focus solely on preparing delivery food (a concept referred to as cloud or ghost kitchens).
The process of food delivery is then executed by so-called Dashers, the company's riders that it hires on a contractual basis. As contract workers, Dashers are not employees of the company. Instead, they only get paid whenever actively delivering.
Compensation is based on a multitude of factors, including:
- base pay, which is determined by time worked, distance traveled, and desirability of the order
- promotions, being higher compensation in peak times and rewards for challenges hosted by DoorDash (for instance delivering a certain amount of orders in a given time frame)
- tips, which Dashers can fully keep
As the operator of the marketplace, DoorDash also takes care of the payment process. When placing an order, customers pay DoorDash directly. Afterward, the restaurants can claim the money they earned on the platform minus fees (more on that later).
Apart from restaurant food, users can also order convenience store products from the likes of Walgreens or 7-Eleven via a product called DashMart.
A Short History Of DoorDash
DoorDash was founded in 2013 by Stanford alumni Tony Xu, Stanley Tang, Evan Moore, and Andy Fang. During that time, food delivery platforms were only listing the restaurants, which in turn had to conduct deliveries by themselves.
This often resulted in the inability of restaurants to deliver the food fast enough. In some cases, orders had to be canceled because the demand was simply too high.
Into the picture comes DoorDash. Initially, the company started out as PaloAltoDelivery.com to test the model within a condensed region (Stanford, as well as many big tech companies like Apple, are situated in that area).
A couple of hundred orders later, the founders had all the confirmation they needed. They rebranded into DoorDash and joined esteemed startup accelerator Y Combinator.
Due to the increased level of convenience, the company was able to expand into new markets with lightspeed. By 2015, two years after the company's foundation, DoorDash was serving over 18 cities across the United States while skyrocketing to a valuation of over $600 million.
One of the company's success formulas is based on the fact that every full-time employee (not to be mistaken with the contract workers) has to work as a Dasher at least once every month. This creates a constant feedback loop and allows the company to tweak the product experience wherever necessary.
Nonetheless, the growth of DoorDash has not been without troubles. Similar to other on-demand services like Uber and Deliveroo, the company has faced repeated lawsuits for allegedly misclassifying drivers as contract workers.
The mounting public pressure for the way these on-demand giants were dealing with their contractual workers led to a financial down round of DoorDash in 2016. Luckily, a prominent investor came to the rescue to decrease the mounting financial pressure.
In 2018, Softbank (lead investor in "success stories" such as WeWork or dog-walking startup Wag) led a $535 million round, giving DoorDash the necessary war chest to take on its rivals in the heated food delivery market. This allowed DoorDash to capture 34% of the US market in 2019, effectively taking the top spot amongst its rivals.
DoorDash used that clout to go after the likes of Amazon and Instacart with the launch of DashMart in August 2020.
The move fits well with the company's Drive product, which is a white-label delivery solution used by the likes of Walmart or Denny's. With Drive, other businesses can utilize DoorDash's fleet of drivers to offer their own delivery services.
On its road to dominance, the company made sure to collect some heatwaves for its growth-at-all-cost ethos. In 2019, its drivers sued DoorDash for using the customer tips to subsidize their pay. The company reacted to the public backlash by changing its tipping policies, effectively allowing drivers to receive all of the tipped amount.
Unfortunately, the driver's efforts to up their rights appear to have taken a huge step back. In November 2020, voters in California approved, with 56 percent of the vote, the application of Proposition 22. With Prop-22, gig workers remain classified as indepdent contractors instead of employees.
On the backbone of that vote and the increased demand for online food delivery during the pandemic, DoorDash finally decided to IPO. The company filed confidentially with the SEC in November 2020 and went public a month later.
Today, DoorDash is available in more than 4,000 cities across the United States, Canada, and Australia. Additionally, more than 200,000 drivers are delivering food for the company on an on-demand basis.
How Does DoorDash Make Money?
DoorDash makes money via commissions, delivery and service fees, a white-label logistics service (called Drive), a premium subscription plan (called DashPass), and a catering service for other businesses.
Let's take a closer look into how DoorDash manages to monetize its user base and how the company effectively became America's go-to app for all things food delivery.
Commissions
DoorDash charges restaurants a variable percentage fee for every order that is made through its platform. This variable amount is subtracted automatically whenever an order is made.
In April 2021, DoorDash introduced a tiered commission structure. Under the new scheme, restaurants either pay 15 (Basic), 25 (Plus), or 30 (Premier) percent commission.
Different benefits are available depending on what plan a restaurant opts into. For instance, Plus grants restaurants a greater visibility on the app and access to DashPass users. A detailed overview of the fee structure can be found here.
Similarly, DoorDash also charges commissions when users order convenience products. In August 2020, it launched DashMart, which allows customers to order almost any product, ranging from toilet paper to shampoo.
DashMart partners include 7-Eleven, CVS, Walgreens, Wawa, and many more. The service competes against the likes of Gopuff and Postmates.
Nevertheless, the commissions that it charges for those deliveries are much lower due to the negotiating power those partners possess.
Delivery & Service Fees
On top of the restaurant commission, DoorDash earns money by charging customers for delivery as well as various service efforts (including marketing, app maintenance, and so forth).
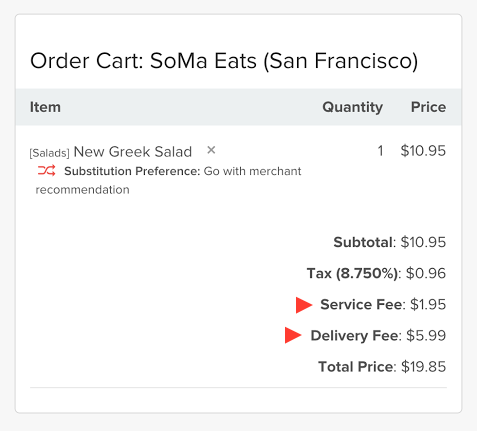
Delivery fees often range between $6-8, depending on the distance and current demand. Delivery fees are used to compensate drivers, but the company does not publicly disclose how much of that money lands in the driver's pockets.
Service fees are calculated as a percentage of the order subtotal. The service fees allow them to cover a variety of costs, including technology development, marketing, and payment processing.
DashPass
DashPass by DoorDash is a subscription service that gives customers the ability to save money on delivery and service fees.
By paying a flat $9.99 every month, customers will not have to pay delivery fees for orders above $12. Furthermore, service fees are charged at a reduced rate.
Notably, not every restaurant is part of the DashPass offer. Similar to other subscription services like Netflix, customers have the ability to cancel at any time.
DoorDash claims that customers will be able to save an average of $4-5 per order when being subscribed to DashPass.
The subscription service is tailored to customers who repeatedly use the DoorDash app for their meal deliveries.
Drive
Drive is a white-label logistics service that allows other restaurants to tap into DoorDash's fleet of drivers.
It is aimed at merchant that already generate demand through their own platform but cannot always fulfil the demand. These include customers like Denny's or Wing Stop.
Pricing is available upon request. In all likeliness, these businesses pay DoorDash a fee for every order that the company fulfils.
DoorDash For Work
DoorDash for Work allows companies to subscribe their employees to DashPass. The service is aimed at employees that were forced to work from home because of the pandemic.
DoorDash generates revenue from the subscriptions as well as the various fees it collects for the orders it facilitates.
DoorDash Funding, Valuation & Revenue
According to Crunchbase, DoorDash has raised a total of $2.5 billion in 12 rounds of funding. During its latest Series H round, which was announced in June 2020, the company raised $400 million at a valuation of $16 billion.
In December 2020, the company was able to raise another $3.4 billion during its IPO. DoorDash hit the public markets with a valuation of $39 billion.
They went through the typical IPO pop, which allowed the stock to soar to $66 billion. The business is currently valued at around $53 billion.
Investors into the company include the likes of the SoftBank Vision Fund, Sequoia Capital, Kleiner Perkins, Temasek Holdings, Darsana Capital Partners, and many others.
The company has generated revenues of $885 million for the fiscal year 2019 according to its S-1 filing. In the first 9 months of 2020, DoorDash recorded an income of $1.916 billion, up almost 400 percent from the $587 million it made in 2019 over the same timespan.
DoorDash remains an unprofitable company, which was mainly driven by the pandemic, despite the exponential growth. It recorded a net loss of $667 million for 2019 while in the first 9 months of 2020, it still lost $147 million.
For reference: DoorDash competitor Grubhub posted revenues of $1.3 billion for the fiscal year 2019. Usage estimates meanwhile show that DoorDash has a market share of 34 percent amongst app users while Grubhub clocks in at only 24 percent.
How Much Money Does Doordash Make
Source: https://productmint.com/the-doordash-business-model-how-does-doordash-make-money/
Posted by: williamsreptit.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Much Money Does Doordash Make"
Post a Comment